Industries
Flexible and printed electronics has successfully entered important industry sectors. From consumer electronics, internet of things and healthcare to automotive, smart packaging and buildings: Printed electronics is now globally being applied in numerous products and industries. The focus industries OE-A is looking into, which are also represented in the OE-A Roadmap, can be found below.

Automotive & Mobility
A key trend in the automotive industry is the tendency for motor vehicles to become “smarter” and to have more and more information interfaces with the driver or passenger, all while being lightweight and taking up very little installation space.
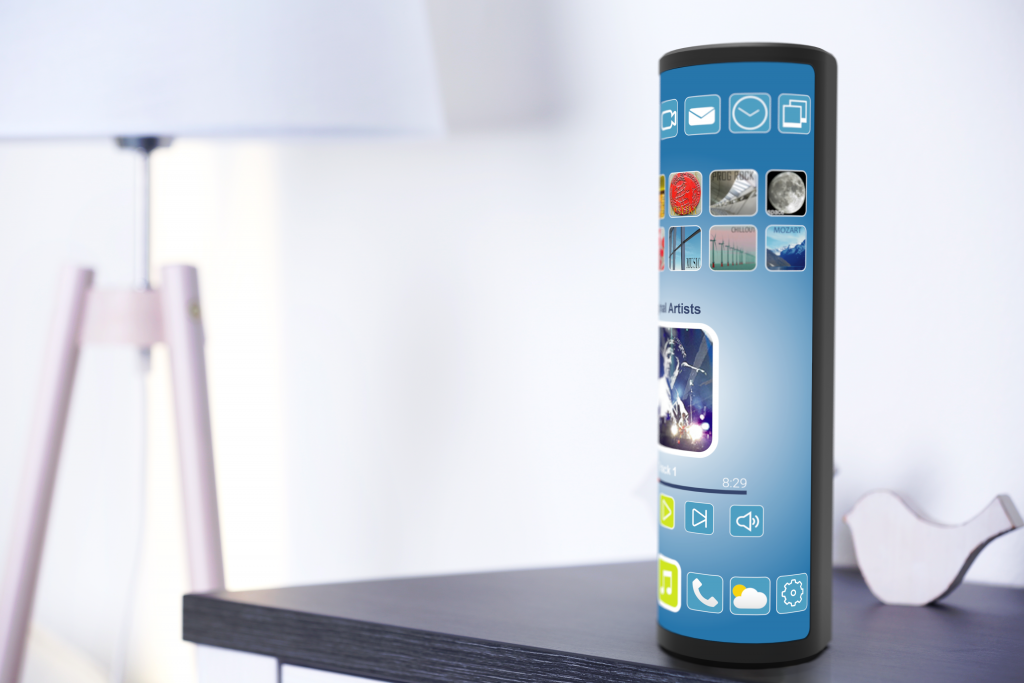

Consumer electronics
Consumer electronics is currently one of the largest industries in which printed electronics is being applied. In this case, consumer electronics refers to both information and entertainment devices such as phones, computers, tablets, TVs and stereos, and to white goods such as refrigerators and washing machines.
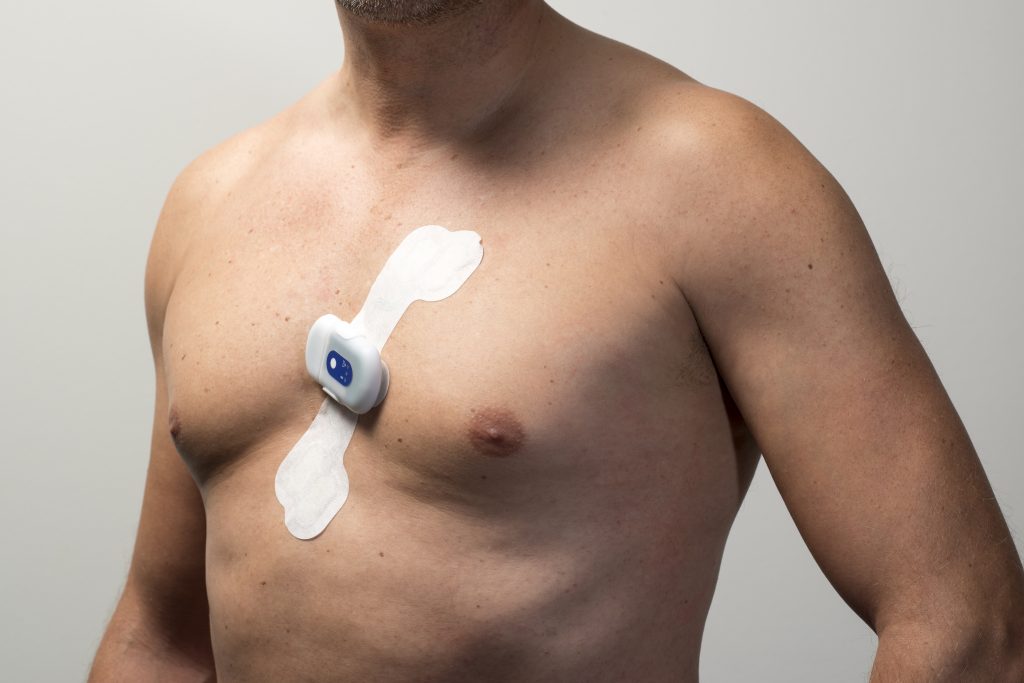
Healthcare & Wellbeing
The industry associated with healthcare and wellbeing (not just pharmaceuticals) has grown tremendously in recent years, both due to technological advances and to an aging society in many countries. Flexible and printed electronics plays an increasingly important role in this industry.

Internet of Things
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a broad term describing the increasing integration of intelligence and wireless connectivity into objects that previously did not have such functionality, such as machines, (sometimes referred to as “Industry 4.0”), automobiles, appliances, but also everyday objects with embedded sensors, processors and displays, sometimes being referred to as the “Internet of Everything” (IoE).

Printing & Packaging
The printing and packaging industry is being transformed as packaging becomes more than just an object to hold and printing becomes increasingly functional.
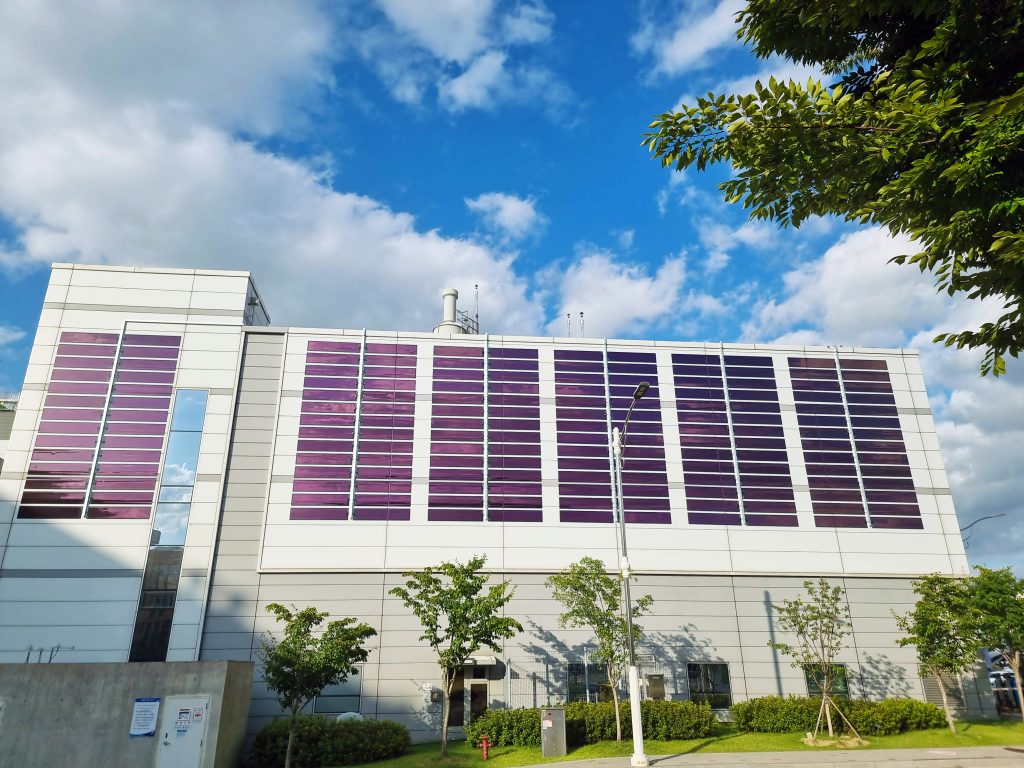

Smart Buildings
The construction industry is being transformed by the trend of smart buildings. Sensors embedded in construction materials for monitoring both during and after construction can measure and control material quality, energy usage anda range of other important factors for wellbeing such as humidity, mold or gases.
Applications
The number of possible application areas of printed electronics is increasing: Due to continuous development, the individual components become more efficient. The areas of application are therefore complex and not easy to be summarized. Some important elements of printed electronics are explained in more detail below.
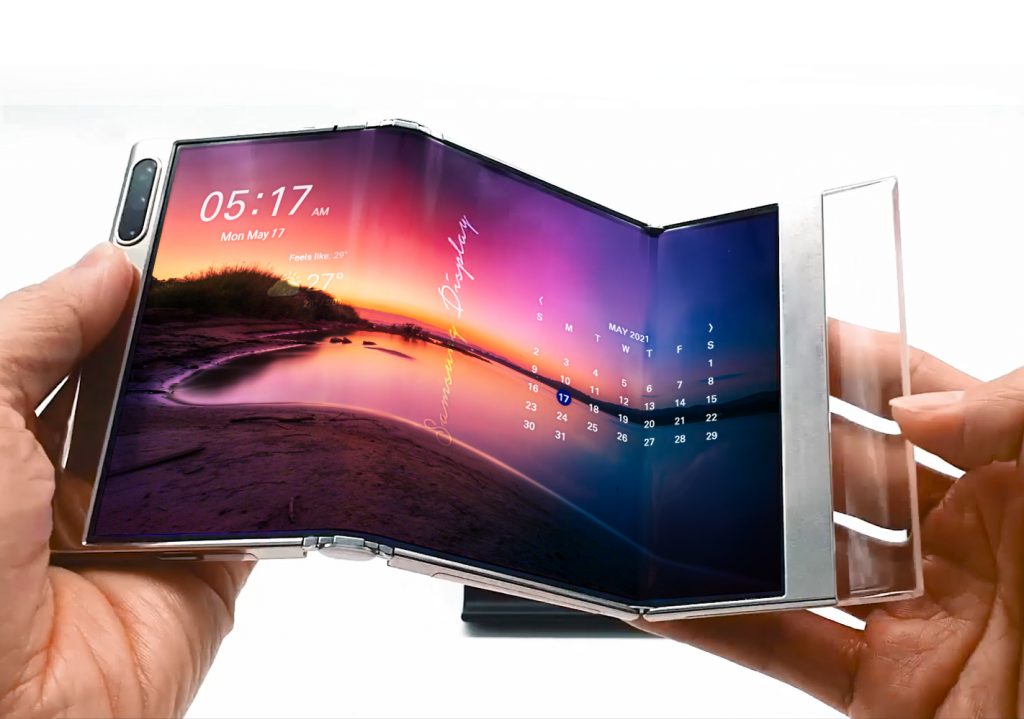

OLED & Flexible Displays
Organic light emitting diodes (OLEDs) are full area and homogenous light, that can be flexible, based on the production process.
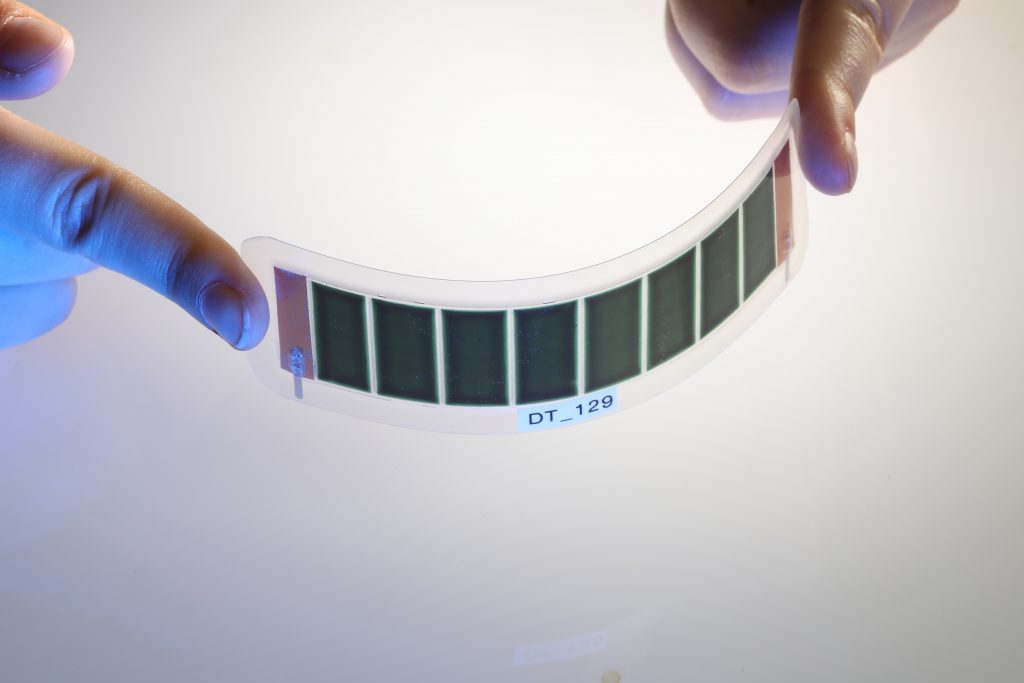
OPV
Organic and printed photovoltaics (OPV) is an emerging, clean energy technology enabling a wide range of applications.

NFC & RFID
Nearfield communication (NFC) and radio frequency identification (RFID) are transmission standards for contactless data transmission using electromagnetic induction.
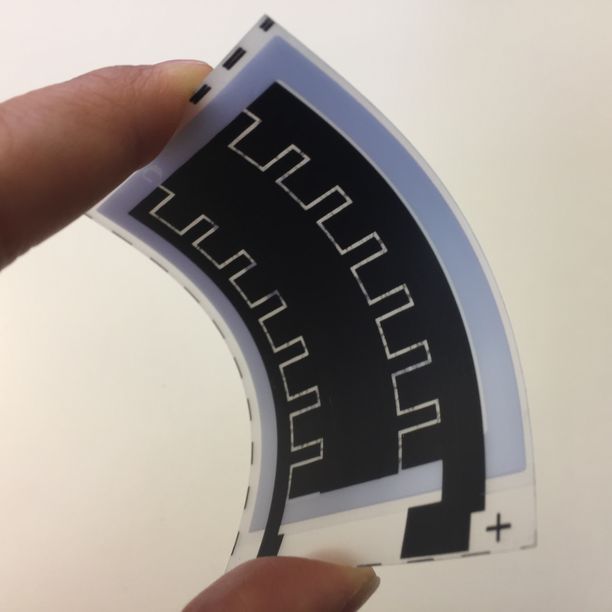
Flexible Battery & Supercapacitor
Flexible batteries and supercapacitors are key technologies for next generation energy storage.

Hybrid Systems
Hybrid printed electronics combines printed functionality with conventional electronic components with the aim to use the best of both worlds: Large area flexibility of printed electronics and high-performance of conventional electronics.





